Your factory is producing, but something feels off.
Orders are piling up. Delivery dates are slipping. Costs are rising. Yet your machinery seems to be running fine.
Here’s the thing—bottlenecks aren’t always obvious. A bottleneck is when one part of your production process slows down the entire system. It could be a single slow machine. It could be waiting for materials. It could be a temporary overload that nobody noticed until it cascaded into bigger problems.
The real problem? By the time you notice a bottleneck, you’ve already lost money.
That’s where artificial intelligence comes in. AI can spot bottlenecks before they become costly problems. Using machine learning and real-time data from your factory floor, AI systems detect constraints, predict failures, and suggest fixes—all automatically.
This article explains how AI detects manufacturing bottlenecks, why it matters for your business, what real companies are doing to stay ahead, and what you need to know about implementation challenges. For deeper context on manufacturing optimization frameworks, see our comprehensive guide to Theory of Constraints software.
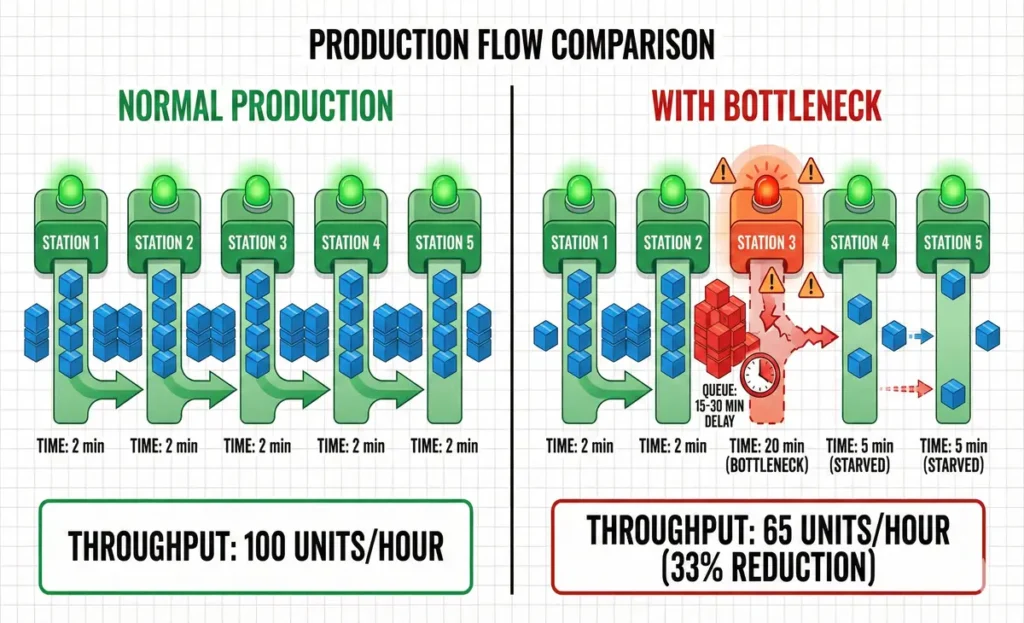
What Is a Manufacturing Bottleneck?
A bottleneck is any point in your production process that slows down everything else.
Think of it like a highway with three lanes. If one lane suddenly gets clogged, the entire road slows down—even the lanes that are running smoothly.
In manufacturing, bottlenecks look like this:
- Machine slowdown: One piece of equipment runs slower than others, delaying the entire line.
- Resource shortage: You run out of parts, causing workers to wait.
- Quality issues: Defective products need rework, backing up the line.
- Scheduling conflicts: Poor planning causes idle time or overwork at specific stations.
- Equipment failure: An unexpected breakdown stops everything.
The Theory of Constraints (TOC) teaches us that every system has at least one bottleneck. The goal isn’t to eliminate all bottlenecks—that’s impossible. The goal is to identify them, manage them, and minimize their impact.
That’s exactly what AI does.
How Traditional Bottleneck Detection Falls Short
Traditionally, managers spot bottlenecks through:
- Visual inspections: Walking the factory floor and watching for delays.
- Manual reports: Waiting for production teams to flag problems.
- Historical data: Analyzing past production records—sometimes weeks later.
- Gut feeling: Using experience to guess where the problem might be.
The problem: By the time you notice, the bottleneck has already cost you thousands in lost throughput, rework, and missed deadlines.
You’re playing catch-up instead of getting ahead.
AI-powered bottleneck detection changes this. It works 24/7, processes data instantly, and predicts problems before they happen.
How AI Actually Detects Manufacturing Bottlenecks
AI bottleneck detection works in five steps:
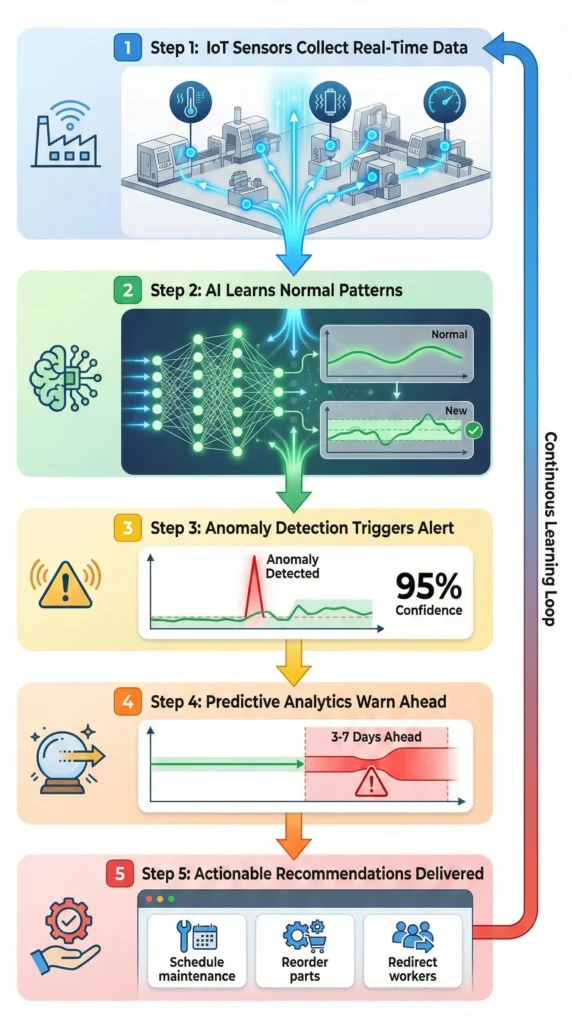
Step 1: Real-Time Data Collection from IoT Sensors
Your factory floor is already full of data—you just need to tap into it.
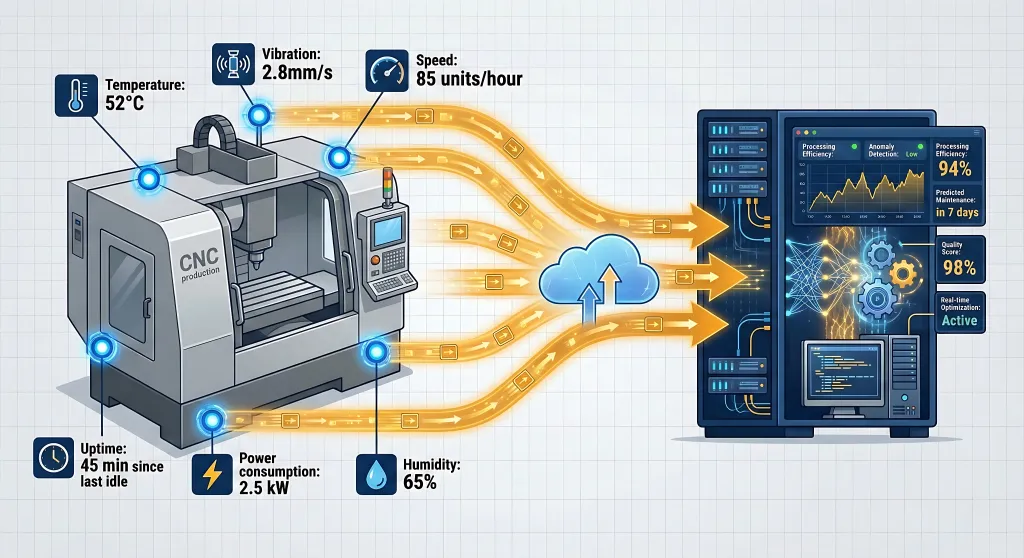
IoT sensors on machines measure:
- Temperature and vibration levels
- Machine speed and load percentage
- Output rates (units produced per hour)
- Idle time vs. active running time
- Energy consumption
- Pressure and humidity
These sensors feed data continuously to an AI system. Instead of looking at what happened yesterday, AI sees what’s happening right now.
Step 2: Pattern Recognition and Anomaly Detection
Once the AI system has data, it looks for patterns.
During the training phase, the AI learns what “normal” looks like. It builds a baseline for your specific production line.
- Normal machine temperature: 45-55°C
- Normal output rate: 120 units per hour
- Normal vibration level: 2.5mm/s
Then, it watches for anything that deviates from this baseline.
When something is different—it’s flagged as an anomaly.
Example: If your machine temperature jumps to 75°C (above normal), the AI doesn’t just note it. It asks: “Does this temperature spike happen before production slowdowns?” If the answer is yes, the AI adds it to its detection model.
The AI also looks for correlations between different factors. For instance:
- High humidity + High machine load = Equipment failure in 3 days
- Upstream machine overproduction + No storage space = Bottleneck in 2 hours
Machine learning finds these hidden patterns automatically. Important note: Initial accuracy is lower—typically 50-70% in the first month as the model learns your specific equipment.
Step 3: Predictive Analytics—Seeing the Future
This is where AI shifts from detecting problems to preventing them.
Instead of telling you “You have a bottleneck right now,” AI says “You will have a bottleneck in 4 hours unless you take action.”
It does this using predictive models trained on historical data. The AI learns:
- Which combinations of factors lead to bottlenecks?
- How long before the bottleneck gets critical?
- What are the early warning signs?
Real example: An AI system notices that whenever a supplier delivers late AND inventory is low, the assembly line gets backed up 18 hours later. So when both conditions appear, the system immediately alerts you: “Reorder parts now to prevent delays.”
Step 4: Instant Alerts and Recommendations
When AI detects a bottleneck (or predicts one), it doesn’t just sound an alarm.
It tells you what to do about it.
Smart recommendations might include:
- “Machine 4 is overheating. Schedule maintenance now.”
- “Inventory of Part XYZ is running low. Reorder from Supplier B (faster delivery).”
- “Assembly station 3 is 2 hours behind. Redirect 2 workers from station 5.”
- “Quality defect rate spiked. Run diagnostic on Machine 2.”
Your team gets actionable insights, not just warnings.
Step 5: Continuous Learning and Improvement
AI systems get smarter over time.
Every time your team takes action on an AI recommendation, the system learns whether that action worked. Did it prevent the bottleneck? Did it reduce downtime? The AI adjusts its models accordingly.
This creates a feedback loop:
Data → Analysis → Prediction → Action → Result → Improved Models → Better Predictions
Key AI Methods Used for Bottleneck Detection
Different AI techniques work for different types of bottlenecks.
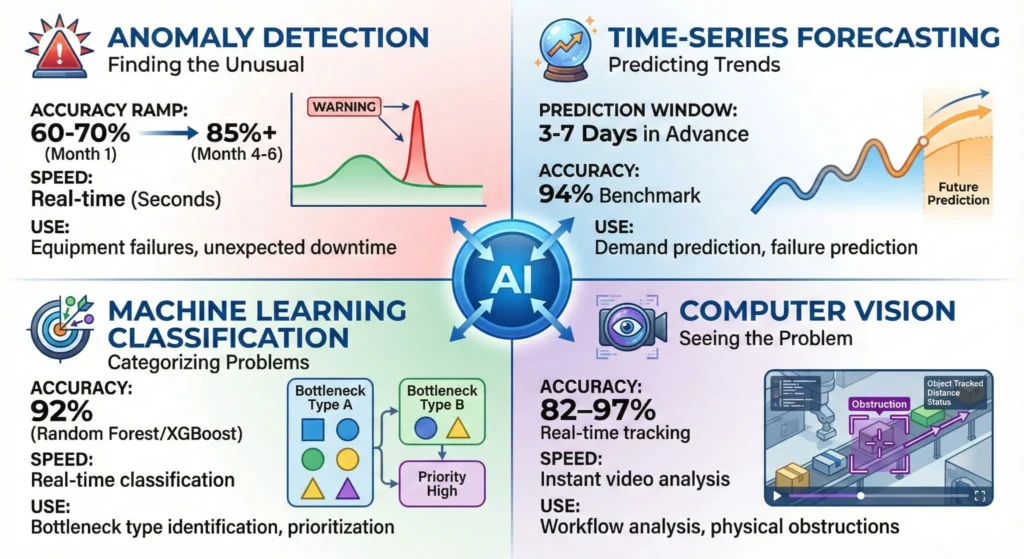
Anomaly Detection (Finding the Unusual)
What it does: Anomaly Detection learns what normal looks like, then spots anything abnormal.
Best for: Detecting sudden equipment failures, unexpected downtime, sudden quality drops.
How it works: The AI system builds a “normal range” for each metric. When data falls outside that range, it’s flagged.
Example: Your conveyor belt normally moves at 50 meters per minute. Suddenly it drops to 35 m/min. Anomaly detected.
Real-world accuracy: Starts at 60-70%, reaches 85%+ after 4-6 months of learning.
Time-Series Forecasting (Predicting Trends)
What it does: Analyzes historical data patterns to forecast future values.
Best for: Predicting when equipment will fail, predicting production slowdowns, predicting parts shortages.
How it works: The AI looks at trends over time. If vibration levels have been rising steadily for a week, it calculates when they’ll exceed safe limits.
Example: Bearing vibration increases 0.5mm/s every week. At the current rate, it will reach failure threshold in 3 weeks. Schedule maintenance proactively.
Realistic prediction window: 3-7 days in advance, accuracy improves with time.
Machine Learning Classification (Categorizing Problems)
What it does: Sorts bottlenecks into categories (long-term vs. short-term, critical vs. minor).
Best for: Prioritizing which bottlenecks need immediate attention.
How it works: The AI uses historical data to learn what causes different types of bottlenecks, then classifies new issues accordingly.
Example: “This bottleneck is a long-term resource constraint (parts shortage) that will take 5 days to fix. This other one is a short-term equipment hiccup that will resolve itself in 30 minutes.”
Computer Vision and Video AI (Seeing the Problem)
What it does: Analyzes video feeds from cameras to spot workflow issues.
Best for: Detecting workers standing idle, materials stacked incorrectly, equipment misalignment, safety issues.
How it works: AI trained on thousands of factory floor videos learns what efficient work looks like, then detects deviations.
Example: Computer vision spots that workers at Station 5 are waiting for parts 40% of the time. This is a resource bottleneck.
Real Companies Using AI for Bottleneck Detection
You don’t have to be a tech giant to use AI for bottleneck detection. But let’s see how industry leaders are doing it:
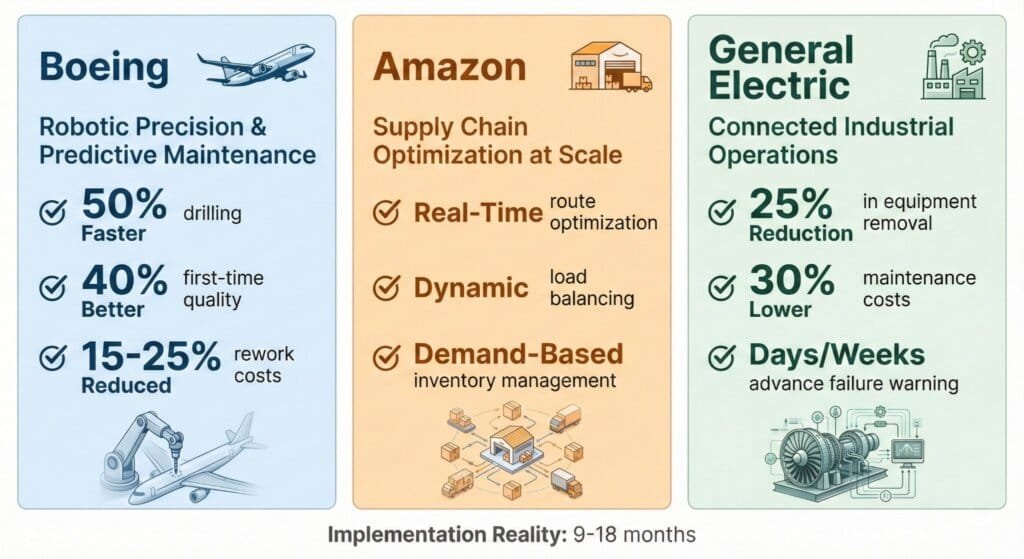
Boeing: Robotic Precision and Predictive Maintenance
Boeing manufactures aircraft—incredibly complex products with millions of components.
How Boeing uses AI:
- Robotic drilling and fastening: Automated systems perform repetitive assembly tasks 50% faster than humans, reducing bottlenecks in drilling and fastening operations specifically.
- Digital twins: Virtual simulations of aircraft and production lines help identify bottlenecks before they happen on the physical floor.
- IoT sensor networks: Sensors across all production lines monitor equipment health, temperature, and performance in real-time.
- Predictive analytics: AI predicts equipment failures, allowing Boeing to schedule maintenance before breakdowns occur.
- Quality improvements: AI-driven first-time quality has improved by 40%, reducing rework bottlenecks.
Boeing manufactures aircraft through incredibly complex production processes. The company uses AI for predictive maintenance and robotic precision to improve drilling speed and reduce rework costs.
Result: Reduced rework costs (15-25% reduction), faster production cycles, and higher quality aircraft.
Important: These improvements happened over 12-18 months of implementation, not immediately.
Amazon: Supply Chain Optimization at Scale
Amazon doesn’t just sell products—it manufactures warehouse automation systems and logistics networks.
How Amazon uses AI:
- Real-time route optimization: AI adjusts delivery routes dynamically based on traffic, weather, and demand.
- Load balancing algorithms: AI distributes work across warehouses to prevent any single location from becoming a bottleneck.
- Predictive inventory management: AI forecasts demand and adjusts stock levels automatically, preventing shortages.
- Automated quality control: Computer vision systems catch defects early before they reach customers.
Amazon applies AI across its logistics network through real-time route optimization and load balancing that prevents bottlenecks in warehouse operations.
Result: Faster deliveries, lower costs, and ability to handle demand surges (like holiday shopping) without service breakdowns.
General Electric: Connected Industrial Operations
GE applies AI across dozens of manufacturing facilities worldwide.
Key applications:
- Asset health management: IoT sensors on every machine feed into AI systems that predict failures with days or weeks of notice.
- Production scheduling optimization: AI adjusts production schedules to balance workloads and prevent machine overuse.
- Energy efficiency: AI identifies energy waste patterns and suggests optimizations.
- Reliability improvements: GE’s predictive maintenance reduces unscheduled equipment removals by 25% and cuts maintenance costs by 30%.
General Electric applies AI across manufacturing facilities worldwide using IoT sensors and predictive analytics to reduce unplanned downtime.
Implementation reality: These results took 9-12 months to achieve across their facilities.
Key Manufacturing Metrics That AI Monitors
AI doesn’t just look for vague “slowdowns.” It monitors specific, measurable KPIs:
ISO 9001 manufacturing quality standards measure First Pass Yield (FPY) as a critical metric. AI bottleneck detection helps improve FPY by stabilizing processes.
| Metric | What It Measures | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Throughput | Units produced per hour | Higher throughput = better capacity utilization |
| Cycle Time | Time to complete one production cycle | Shorter cycle time = faster delivery |
| On-Time Delivery (OTD) | % of orders delivered by promised date | Critical for customer satisfaction |
| Lead Time | Time from order to delivery | Shorter lead time = better competitiveness |
| Equipment Downtime | Total hours machines are inactive | Less downtime = more production |
| First Pass Yield (FPY) | % of products made correctly first time | Fewer defects = less rework |
| Machine Utilization Rate | % of available time machine is actually producing | Higher = better efficiency |
| Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) | Combined measure of availability, performance, quality | Industry gold standard for manufacturing health |
AI continuously monitors all these metrics and flags when they deviate from targets.
Benefits of AI Bottleneck Detection: What You Actually Get
Using AI to detect manufacturing bottlenecks delivers real, measurable results—but timelines matter.

Reduced Downtime
The problem: Unexpected equipment failure stops your entire line.
AI solution: Predicts failures 3-7 days in advance, so you can schedule maintenance during planned downtime.
Impact: Typical improvement is 25-40% reduction in unplanned downtime (measured after 6-12 months of full implementation).
Realistic timeline: First 3 months shows minimal improvement (0-15%). Real benefits start month 4.
Increased Throughput
The problem: Bottlenecks limit how much you can produce.
AI solution: Identifies constraints and suggests optimizations (speed up slow machine, rebalance workload, improve scheduling).
Impact: Increases production output by 15-30% (after full implementation and team adoption).
Realistic timeline: Measured over 6+ months as team learns to trust and act on AI recommendations.
Lower Operational Costs
The problem: Bottlenecks = wasted labor, materials, energy.
AI solution: Prevents unnecessary rework, reduces idle time, optimizes resource allocation.
Impact: Cuts production costs by 10-20% through efficiency gains.
Realistic timeline: Cost reduction begins month 5-6 as system optimizes.
Better Product Quality
The problem: Rushed processes due to bottlenecks = higher defect rates.
AI solution: Stable, optimized processes = consistent quality.
Impact: Reduces defect rate by 5-15%, fewer customer complaints.
Note: Conservative estimate—sources show 15-40% improvements possible with mature systems.
Faster Delivery Times
The problem: Bottlenecks delay orders.
AI solution: Eliminates constraints, speeds up production, improves scheduling.
Impact: Reduces lead time by 10-25%, customers get products faster.
Proactive, Not Reactive
The problem: Traditional management reacts after problems happen.
AI solution: Predicts problems before they impact production.
Impact: You manage your factory, instead of firefighting constantly.
How to Get Started with AI Bottleneck Detection
You don’t need to overhaul your entire operation. Here’s a practical approach:
Step 1: Assess Your Current Situation
- Identify your worst bottlenecks: Where do you lose the most time, quality, or money?
- Collect baseline data: What are your current throughput, cycle time, downtime metrics?
- Inventory your data sources: What sensors, systems, and data do you already have?
Step 2: Start Small (Pilot Project)
Don’t try to monitor your entire factory with AI immediately.
Pick one bottleneck that costs you the most money. Set up sensors and AI monitoring for that specific area.
Example: “Our paint station is our slowest step. Let’s put sensors there first.”
Step 3: Choose the Right Tools
You have options:
- TOC software platforms: Specialized software built for Theory of Constraints, with AI modules.
- Industrial IoT platforms: General-purpose systems like Siemens MindSphere, GE Predix.
- Custom AI solutions: Hire a consultant to build a system tailored to your factory.
- Cloud-based analytics: Solutions like Amazon AWS, Microsoft Azure offer manufacturing modules.
Start with: Software designed specifically for manufacturing. TOC-based platforms are ideal because they’re built to find constraint management solutions.
Step 4: Integrate with Existing Systems
Your AI system needs to connect with:
- Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES): Real-time production data
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Inventory, scheduling, supplier data
- SCADA/PLC systems: Machine-level control and monitoring
Important note on integration: Modern systems (built in last 10 years) integrate straightforwardly. Legacy equipment (20+ years old) may require 20-30% additional budget for APIs, firmware updates, or workarounds. Plan accordingly.
Step 5: Train Your Team and Take Action
An AI system is only valuable if your team actually uses the recommendations.
- Training: Show operators and managers how to interpret alerts.
- Define workflows: What action should we take when AI predicts a bottleneck?
- Measure results: Track improvements in throughput, quality, costs.
Common Challenges & Limitations: What To Expect
Understanding implementation challenges separates successful projects from failures. Here’s what manufacturers actually encounter:
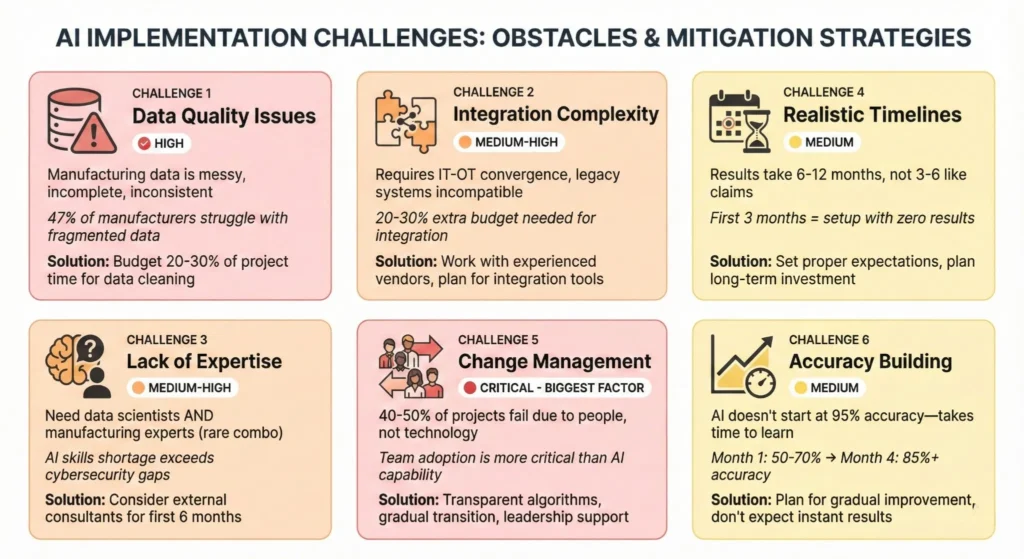
Challenge 1: Data Quality Issues
The reality: Manufacturing data is messy, incomplete, and inconsistent.
- Missing sensor readings break models
- Different equipment formats data differently
- Legacy systems store data in incompatible formats
- Humidity, dust, and temperature affect sensor accuracy
What research shows: 47% of process industry leaders are still wrestling with fragmented, low-quality datasets that kill digital projects.
How to manage it: Budget 20-30% of project time for data cleaning. Don’t expect AI to work with raw, dirty data.
Challenge 2: Integration Complexity
The reality: Connecting your AI system to existing operations is harder than it sounds.
- Requires IT-OT convergence (technology team + operations team working together)
- Legacy systems don’t have APIs (application programming interfaces)
- Firewall rules restrict data flow
- Each facility may have different systems
How to manage it: Work with vendors experienced in your industry. Budget 20-30% extra for integration tools and professional services.
Challenge 3: Skills Gap
The reality: You need both data scientists AND manufacturing domain experts—a rare combination.
Research shows: AI skills shortage now outstrips even cybersecurity gaps.
- Data scientists don’t understand manufacturing
- Manufacturing engineers don’t understand machine learning
- Training new staff takes 3-6 months
How to manage it: Consider external consultants for the first 6 months, then build internal capability.
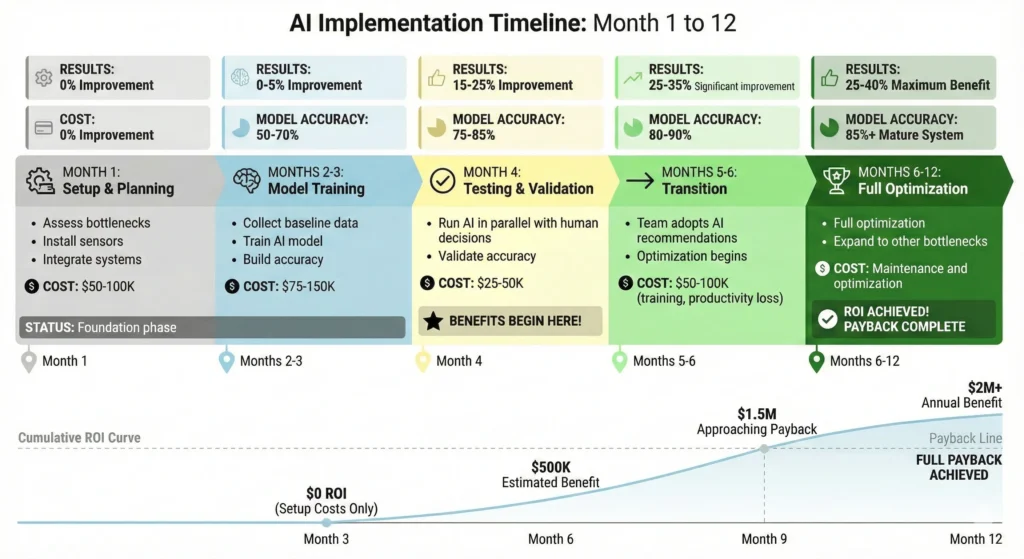
Challenge 4: Timeline Reality
The reality: Results take longer than most articles claim.
Realistic implementation timeline:
- Month 1: Setup and planning (NO results yet)
- Assess bottlenecks, install sensors, integrate systems
- Cost: $50-100K
- Months 2-3: Data collection and model training (0-5% improvement)
- Collect 4-6 weeks of baseline data
- Train AI model on your specific equipment
- Model accuracy: 50-70%
- Cost: $75-150K
- Months 4: Testing and validation (15-25% improvement)
- Run AI recommendations in parallel with human decisions
- Validate accuracy on your specific process
- Cost: $25-50K
- Months 5-6: Transition to AI-driven decisions (25-35% improvement)
- Team transitions from monitoring to trusting recommendations
- This is the hardest phase (see Challenge 5)
- Cost: $50-100K (training, productivity loss)
- Months 6-12: Full optimization (25-40% improvement, payback achieved)
- Model fully trained (85%+ accuracy)
- Team confident with recommendations
- Begin expanding to other bottlenecks
Total typical cost: $200K-$400K for mid-size manufacturer
Realistic payback: 9-18 months, not 3-6 months
Challenge 5: Change Management (The Biggest Factor)
The reality: 40-50% of AI projects fail due to people, not technology.
Research shows: Most promising AI pilots stall when leadership, metrics, and mindsets pull in different directions.
The Five Focusing Steps of Theory of Constraints provide a structured framework for identifying and addressing these change management challenges.
Why it happens:
- Operators distrust AI recommendations initially
- Changing work processes creates friction
- Accountability is unclear (who takes responsibility?)
- Workers fear job loss
- Success metrics aren’t clear
Real example of failure:
Month 1-2: Great technical results, AI shows 95% accuracy
Month 3: Operators ignore AI recommendations (don’t trust it)
Month 4: Management cancels project (no behavioral change)
Result: Failed implementation, wasted $300K+
How to prevent it:
- Transparent algorithms: Explain WHY AI makes recommendations
- Gradual transition: Start with suggestions, move to automation slowly
- Win hearts: Show workers how AI helps them (less firefighting)
- Clear metrics: Everyone knows what success looks like
- Leadership support: Executive must champion the change
Challenge 6: Model Accuracy Building
The reality: AI models don’t start at 95% accuracy. They learn over time.
- Week 1-4: 40-60% accuracy (too unreliable)
- Month 2: 60-75% accuracy (starting to help)
- Month 3-4: 75-85% accuracy (becoming reliable)
- Month 4-6: 85%+ accuracy (ready for production)
Why accuracy ramps: AI learns your specific equipment, processes, and conditions. No two factories are identical.
Real Concerns (And How To Address Them)
“Won’t this cost too much?”
Answer: The cost of a bottleneck is always higher than the cost of preventing it. For a $50M revenue factory with 15% downtime:
- Annual cost of downtime: $7.5M in lost throughput
- Implementation cost: $200K-$400K
- ROI: 9.7x return on investment
- Payback period: Month 9-12 typically
Even a small improvement (10% downtime reduction) pays for the system in 2-3 months.
“What about data privacy and security?”
Answer: Industrial AI systems can operate on your own servers (on-premise), not in the cloud. Your data stays internal.
- Manufacturing data is proprietary (trade secret)
- Request: On-premise deployment capability
- Verify: SOC 2 Type II certification from vendor
- Require: Data ownership clause in contract (you own data, vendor doesn’t)
Modern systems also use encryption and secure APIs.
“Do we need to replace our existing systems?”
Answer: No. Most AI platforms integrate with existing equipment using adapters and APIs. You don’t need a complete overhaul.
However: Legacy systems (20+ years old) may require firmware updates, API development, or partial equipment replacement. Budget 20-30% extra for integration.
“Will AI replace our workers?”
Answer: AI takes over repetitive monitoring and prediction. Your team focuses on higher-value decisions and problem-solving.
Most companies find AI creates new roles (data analysts, system managers) while eliminating tedious tasks. Workers spend less time firefighting and more time on strategy.
How AI Fits With TOC and Lean Manufacturing
You might wonder: “Should we use AI, Theory of Constraints, or Lean?”
The answer: All three, together.
Theory of Constraints (TOC):
- Identifies THE bottleneck (critical constraint)
- Manual process, takes weeks/months
- Improves throughput of that constraint
Lean Manufacturing:
- Eliminates waste throughout system
- Continuous improvement everywhere
- Reduces costs generally
AI Bottleneck Detection:
- Identifies bottlenecks in REAL-TIME
- Continuous, 24/7 monitoring
- Detects hidden constraints humans miss
- Combines speed of AI with TOC’s precision
Best practice (Industry Standard):
- Use TOC framework to identify your primary bottleneck
- Use AI to detect it faster in real-time
- Use Lean tools to eliminate waste from that bottleneck
- Repeat the cycle continuously
= Maximum improvement, maximum speed, maximum ROI
Real Example: Calculating Your ROI
Let’s make this concrete with a realistic scenario:
Scenario: Automotive Parts Manufacturer
Current State:
- Annual revenue: $50M
- Current downtime: 15% (should be 8%)
- Excess downtime cost: 7% × $50M = $3.5M/year in lost throughput
- Additional rework costs: $1.5M/year
- Total annual cost of bottlenecks: $5M
AI Implementation:
- Hardware (sensors, gateways): $75K
- Software (license + setup): $100K
- Integration work: $100K
- Training and change management: $50K
- Total first-year cost: $325K
Expected Results (Year 1):
- Downtime reduction: From 15% to 10% (33% improvement)
- Recovered throughput: $1.75M/year
- Reduced rework: $300K/year (20% improvement)
- Total first year benefit: $2.05M
ROI Calculation:
- Benefit: $2.05M
- Cost: $325K
- ROI: 6.3x return on investment
- Payback period: Months 8-10
- Year 2 benefit (ongoing): $2.05M/year
Why this matters: Payback happens before year-end. Easy to justify to CFO.
Key Takeaways
Manufacturing bottlenecks are invisible until they hurt you. AI changes that.
By combining IoT sensors, machine learning, and predictive analytics, AI systems detect bottlenecks in real-time, predict problems before they happen, and recommend specific actions to fix them.
Companies like Boeing, Amazon, and GE are already using AI bottleneck detection to:
- Reduce downtime by 25-40% (with 6-12 month timeline)
- Increase throughput by 15-30% (measured over 6+ months)
- Cut costs by 10-20% (gradual improvements)
- Improve delivery times by 10-25%
The path forward is clear:
- Start with your worst bottleneck (highest cost).
- Deploy sensors and AI monitoring (realistic timeline: 6 months to payback).
- Use AI predictions to guide decisions.
- Measure improvements and expand to other bottlenecks.
- Combine with TOC and Lean for maximum impact.
Important reality check: Success depends on data quality, team adoption, and change management—not just technology. Plan accordingly.
Your competition is already doing this. The question isn’t whether to use AI for bottleneck detection—it’s how quickly you can implement it.
How long does it take for AI to detect a bottleneck?
Can small manufacturers afford AI bottleneck detection?
Do we need advanced sensor technology to use AI bottleneck detection?
How accurate is AI bottleneck prediction?
What if we have multiple bottlenecks happening at once?
Can AI work with legacy manufacturing equipment (20+ years old)?
What’s the biggest reason AI bottleneck projects fail?
How do we measure ROI from AI bottleneck detection?
- Throughput (units per hour)
- Downtime (hours per month)
- Lead time (days to produce)
- Defect rate (%)
- Production costs per unit
Does AI bottleneck detection work with Theory of Constraints (TOC) or Lean?
What about data privacy with AI systems?
How long is the actual payback period for AI bottleneck detection?
Next Steps
Ready to detect and eliminate your manufacturing bottlenecks with AI?
Start here:
- Identify your worst bottleneck: Where does your factory lose the most time or money?
- Calculate the cost: How much is that bottleneck costing you per month? (Multiply revenue × % downtime)
- Explore TOC software: Look into Theory of Constraints platforms with AI modules.
- Request a pilot: Talk to vendors about a small 3-month pilot project on your worst bottleneck.
- Get expert advice: Consult with a manufacturing optimization specialist with TOC experience.
Success factors for your implementation:
- ✓ Realistic timeline expectations (6-12 months to full ROI)
- ✓ Strong leadership support (this is crucial)
- ✓ Quality data sources (assess your data infrastructure)
- ✓ Team training and change management (most important factor)
- ✓ Clear success metrics (everyone understands the goal)


